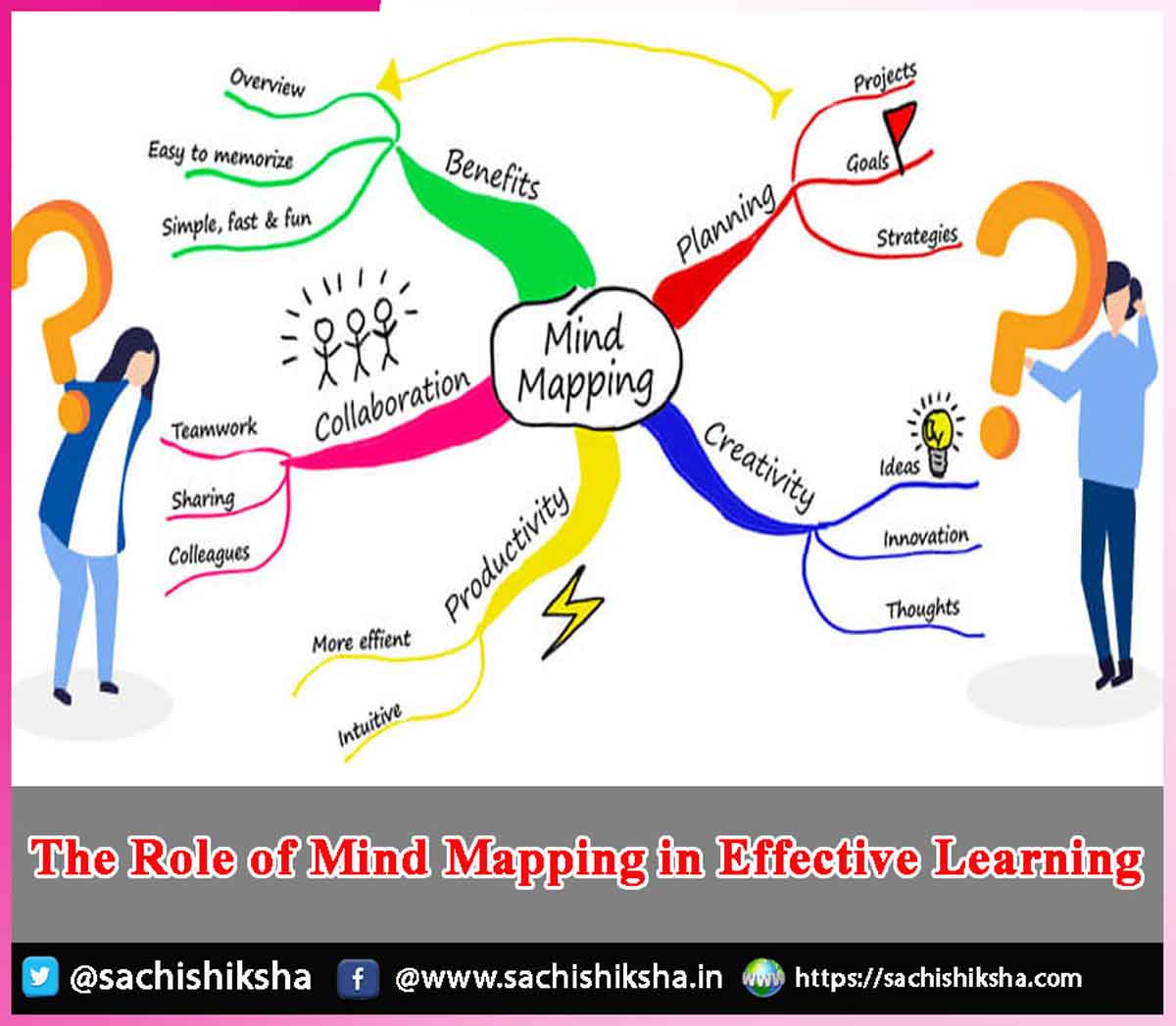
The Role of Mind Mapping in Effective Learning
Introduction: In an age where information overload is a constant challenge, the need for effective learning methods has become increasingly important. Students, professionals, and individuals seeking to improve their cognitive processes require techniques that enhance comprehension, memory retention, and the ability to make connections between disparate ideas. One such technique that has garnered attention for its efficacy is mind mapping.
Table of Contents
What is Mind Mapping?
Mind maps contrast sharply with traditional note-taking methods, where information is often written in linear lists or paragraphs. In mind mapping, the central idea is at the heart of the diagram, and various thoughts and ideas are radiated outward, creating a dynamic, associative structure. This approach encourages creative thinking, enhances memory retention, and fosters deeper understanding.
Cognitive and Psychological Benefits of Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is not just a creative tool; it is deeply rooted in cognitive and psychological principles. By examining how the human brain processes information, we can understand why mind maps are so effective for learning.
Visual Learning and Dual Coding Theory:
According to the dual coding theory proposed by Allan Paivio, the brain processes visual and verbal information separately, but when these two forms of information are used together, learning is more efficient. Mind maps combine words and visuals (such as images, symbols, or different colors), allowing the brain to process and store information in multiple ways. This simultaneous engagement of both verbal and visual systems enhances comprehension and retention.
Facilitating Active Learning:
Mind mapping encourages active learning, a process where learners engage with the material rather than passively receiving information. Creating a mind map requires learners to distill and simplify information, promoting deeper understanding. Active engagement helps reinforce memory, making it more likely that the information will be retained in long-term memory.
Improving Memory Retention:
Mind mapping leverages the brain’s natural ability to form associations. The non-linear structure of mind maps mimics how the brain creates neural connections, facilitating better recall. By organizing information in a way that highlights relationships and hierarchies, learners are more likely to remember complex concepts and retrieve information efficiently when needed.
Enhancing Focus and Reducing Cognitive Load:
One of the challenges of learning is managing cognitive load—the mental effort required to process information. Traditional methods of note-taking often result in cognitive overload, especially when dealing with large amounts of information.
Applications of Mind Mapping in Learning
Mind mapping is versatile and can be applied across various learning contexts, from academic education to personal development and professional environments. The following sections explore how mind mapping can be utilized in these contexts.
Mind Mapping in Education:
In the educational sphere, mind mapping has proven to be a valuable tool for students of all ages. The following are some key areas where mind mapping has a significant impact:
- Note-Taking and Study Aids: Mind mapping can be a powerful tool for students to take notes during lectures. Instead of writing long, linear paragraphs, students can capture key ideas and their relationships. This approach not only saves time but also makes the notes more visually engaging and easier to review later.
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: For complex subjects like mathematics, science, and philosophy, mind mapping helps students break down problems into smaller, more manageable parts. It allows them to explore different solutions and see connections that may not be immediately apparent in a linear format.
- Conceptual Understanding: Mind maps are especially effective in subjects that require a deep understanding of concepts and their interconnections, such as biology, history, or literature. Students can visually organize information, seeing how different historical events or biological processes are interrelated, which aids comprehension.
- Revision and Exam Preparation: Mind maps are excellent tools for exam revision. They provide a holistic view of the subject matter, which can help students identify key themes and important connections between topics. The visual nature of mind maps also makes it easier to recall information during exams.
- Creativity in Learning: Mind mapping can make learning more fun and interactive, particularly in creative subjects like art, design, and writing. By branching out ideas and exploring different possibilities, students can come up with novel solutions and ideas.
Mind Mapping in Professional Settings:
Beyond education, mind mapping is also widely used in professional and business environments. Here are some of the key applications of mind mapping in the workplace:
- Brainstorming and Idea Generation: In meetings or group discussions, mind maps can be an effective tool for brainstorming ideas. By creating a visual representation of ideas, team members can more easily identify patterns, gaps, and connections that may not be immediately obvious through discussion alone.
- Project Management: Project managers use mind maps to outline tasks, timelines, and resources. This helps them visualize the entire scope of a project, identify potential bottlenecks, and allocate resources efficiently.
- Problem-Solving and Decision-Making: Mind maps can help professionals evaluate different options and strategies by mapping out potential outcomes, risks, and benefits. This facilitates more informed decision-making and problem-solving.
- Learning and Skill Development: In the workplace, mind mapping can assist in skill development by helping individuals outline new concepts, technical skills, or training programs. It can also be used to structure personal development plans.
Mind Mapping for Personal Growth and Memory:
Individuals who want to improve their cognitive abilities and memory retention can also benefit from mind mapping. The technique can be applied to various aspects of personal growth, such as:
- Goal Setting: By using mind maps to structure long-term goals and break them down into smaller, actionable tasks, individuals can create a clear path to achieving their objectives.
- Memory Enhancement: Mind maps are particularly effective for individuals looking to improve memory recall. By organizing information visually, learners can create a mental image of the material, making it easier to recall when needed.
- Creative Projects: Artists, writers, and other creative individuals can use mind maps to structure their ideas, plot stories, or organize visual compositions. This approach helps them stay organized while allowing for flexibility and creative exploration.
Practical Tips for Effective Mind Mapping
While mind mapping can be a powerful tool, its effectiveness depends on how it is used. Below are some practical tips for creating effective mind maps:
- Start with a Central Idea: Place the primary concept or topic in the center of the mind map. Ensure that this idea is clear and concise, as it will serve as the foundation for all subsequent branches.
- Use Colors and Images: Incorporating colors and images into your mind map can make it more engaging and easier to remember. Different colors can represent different categories, while images can provide visual cues that reinforce the material.
- Be Flexible: Mind mapping is a dynamic process. As you add new ideas or concepts, feel free to reorganize the map as needed. The goal is to create a structure that works for you and reflects your understanding of the topic.
- Keep It Simple: Avoid cluttering the map with excessive details. Focus on key ideas and how they relate to each other.
Conclusion
Mind mapping is an incredibly powerful tool for enhancing effective learning. By tapping into the brain’s natural processes of association and visualization, mind mapping helps improve memory retention, foster creativity, and promote critical thinking. Whether in education, business, or personal development, mind maps are versatile tools that can be used to organize and simplify complex information. As a result, mind mapping not only aids in learning but also encourages deeper engagement with material, making it a valuable technique for anyone seeking to improve their cognitive processes and learning outcomes.